Phase Shifts in Trigonometry
In mathematics, a trigonometric function can undergo a transformation known as a phase shift. The phase shift is the amount of horizontal displacement of the function from its original position. In simpler terms, it means how far the original graph has moved towards the right or left. A positive phase shift means the graph has moved to the left, while a negative phase shift means the graph has moved to the right.
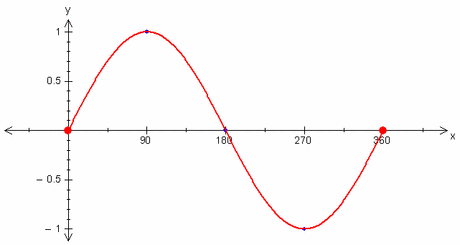
For example, this is the graph of a standard sinusoidal curve (sine wave graph):
For example, this is the graph of a standard sinusoidal curve (sine wave graph):
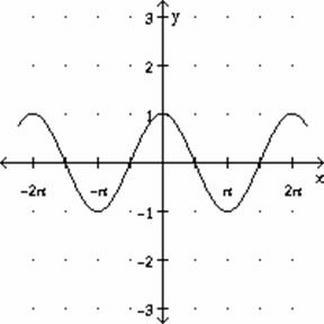
If the graph were to have a positive phase shift of pi, it would then look like this:
This just so happens to be the standard graph of a cosine wave. It is interesting how with one phase shift, a standard sine graph can transform into a standard cosine graph.
Works Cited
Works Cited